Editor's note
Combining the advantages and disadvantages of carbon materials and silicon materials, the two are often combined to maximize their utility. Composite materials can be generally classified into two types according to the type of carbon materials: silicon-carbon conventional composite materials and silicon-carbon new composite materials.
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in computers, mobile phones, EVs, and other portable electronic devices because of their high energy density, high open circuit voltage, and long cycle life. At present, lithium battery is highly commercialized. As one of the four main materials (positive material, anode material, separator, electrolyte) of lithium battery, the performance of anode material has a key impact on battery performance. Shown. At present, lithium battery manufacturers mainly choose graphite materials as anode materials for lithium batteries, and graphite is one of carbon anode materials, including artificial graphite and natural graphite.
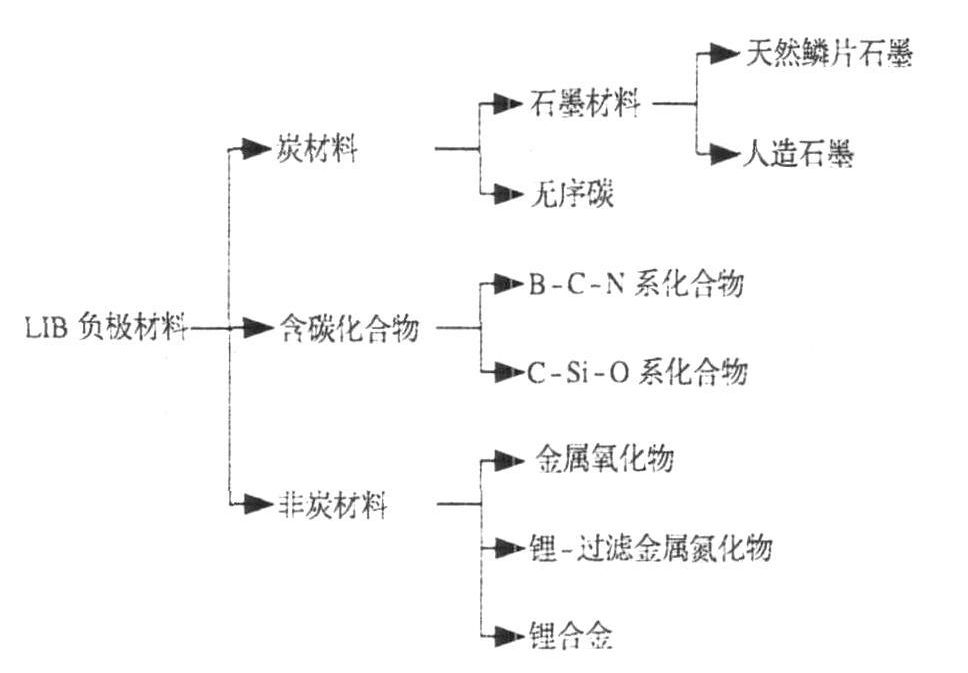
Figure 1. Lithium battery anode material type
Graphite is an ideal anode material, and it is widely used in lithium batteries because of its good cycle stability, excellent electrical conductivity, and a layered structure with good lithium intercalation space. With the continuous improvement of the performance requirements of lithium batteries in the country, the shortage of graphite as a negative electrode material has gradually emerged. For example, the low gram capacity (372 mAh/g), the layered structure is easy to peel off when the number of cycles is large, and the lithium battery is limited. A further increase in specific energy and performance. Researchers are looking for a material that can replace carbon anode materials.
Since silicon can form a binary alloy with lithium and has a high theoretical capacity (4200 mAh/g), it has attracted much attention. In addition, silicon also has a low deintercalation lithium voltage platform (less than 0.5V vs Li/Li+), low reactivity with electrolyte, abundant reserves in the earth's crust, low price, etc. It is a very promising lithium battery. Anode material.
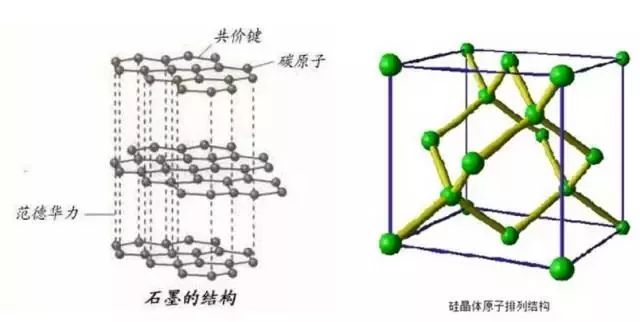
Figure 2. Comparison of structure between graphite and silicon
However, silicon has a fatal defect as a negative electrode of a lithium battery. Lithium ions are extracted from the positive electrode material and intercalated between the crystal lattices inside the silicon crystal during charging, causing a large expansion (about 300%) to form a silicon-lithium alloy. Lithium ions are separated from the crystal lattice during discharge, and a large gap is formed. The use of a silicon crystal alone as a negative electrode material easily causes the following problems:
First, in the process of deintercalation, the volume of the silicon crystal has changed significantly. Such a volume effect easily causes the silicon anode material to be peeled off from the current collector, causing electrochemical corrosion and short circuit of the pole piece exposed foil. Affect the safety and service life of the battery.
Second, silicon carbon is the same main group element. SEI is also coated on the silicon surface during the first charge and discharge. However, the peeling caused by the volume effect of silicon causes repeated destruction and reconstruction of SEI, thereby increasing lithium. The consumption of ions ultimately affects the capacity of the battery.
Combining the advantages and disadvantages of carbon materials and silicon materials, the two are often combined to maximize their utility. Composite materials can be generally classified into two types according to the type of carbon materials: silicon-carbon conventional composite materials and silicon-carbon new composite materials. Among them, traditional composite materials refer to silicon and graphite, MCMB, carbon black and other composites. The new silicon-carbon composite materials refer to silicon and carbon nanotubes, graphene and other new carbon nanomaterials. Different combinations of materials will be formed between different materials. The composite methods/structures of silicon-carbon materials mainly include the following:
First, the walnut structure
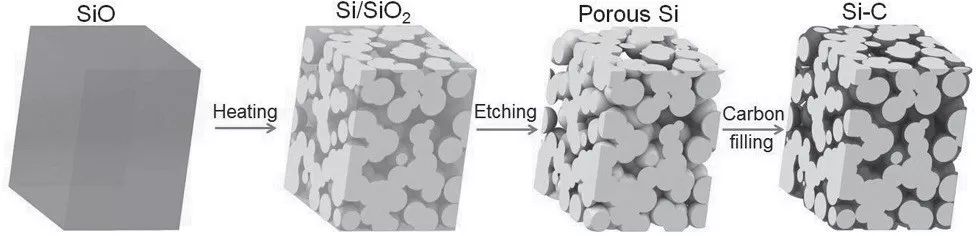
Figure 3. Walnut structure silicon-carbon composite
The silicon-carbon composite material of the walnut structure is formed by making the silicon particles into a porous structure and then filling the carbon material into the porous silicon, as shown in FIG. The nano-micron structure effectively solves the problem of charging and discharging micro and nano silicon materials, and exhibits excellent electrochemical performance. At a current density of 1 A/g, the reversible capacity of 1459 mAh/g can be maintained after 200 cycles of charge and discharge. At a current density of 12.8 A/g, there is still a reversible capacity of 700 mAh/g. The material's excellent energy source is composed of nano-scale silicon particles and a three-dimensional communication channel network of carbon.
Professor Ci Lijie from Shandong University, combined with silicon and graphene, successfully prepared a walnut-like porous silicon/reduced graphene oxide (P-Si/rGO) material by in-situ reduction and dealloying process, which has excellent electrochemical properties. ,As shown in Figure 4.
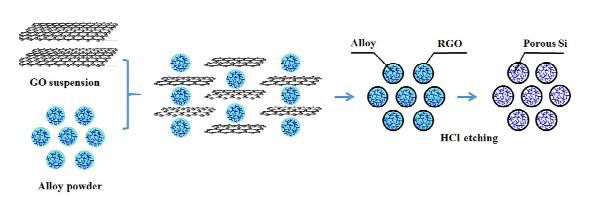
Figure 4. Walnut-like porous silicon/reduced graphene oxide
Second, the cladding structure
The core-shell structure is a common type of composite in which carbon materials are wrapped around the outer layers of silicon particles to form a composite. After the surface of the silicon material is coated with carbon, the conductive property of the material can be enhanced, the carbon material has certain toughness, the agglomeration between the silicon particles and the volume expansion of the material during the process of deintercalating lithium are avoided, and the SEI film is formed on the surface of the carbon material, thereby suppressing The electrolyte destroys the corrosion of the negative electrode material, thereby increasing the cycle life and improving the rate performance. Compared with the silicon carbon material of the walnut structure, the silicon carbon material of the coated structure contains a large amount of silicon, which greatly increases the lithium intercalation space; in addition, the phenomenon of swelling and pulverization of the silicon particles is also greatly reduced.
By carbon coating the silicon material, the core-shell structure is built to help improve the cycle stability of the material. However, when the pyrolytic carbon in the silicon-carbon core-shell structure is coated on the surface of the silicon particles without voids, the volume effect of the silicon lithiation process is too large, which causes the entire core-shell particle to swell and even cause the surface carbon layer to occur. The rupture, the composite structure collapses, and the cycle stability decreases rapidly. In order to solve this problem, some researchers started from the aspect of strengthening the mechanical properties of the shell and designed a double-shell structure, as shown in Figure 5. First, SiO2 is coated on the surface of the silicon particles, and then a layer of carbon material is coated on the surface of the composite particles, which can effectively alleviate the structural changes of the composite material and improve the cycle life of the lithium battery.
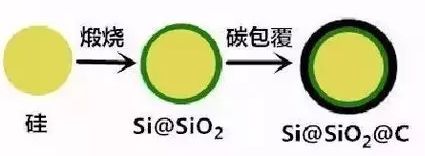
Figure 5. Double-layer cladding structure
Three- and three-element embedded composite structure
Embedded silicon-carbon structures are often found on new silicon-carbon composites such as silicon/CNT and silicon/graphene. Fig. 6 is a schematic view showing the structure of a composite of silicon, carbon material and CNT. First, a silicon film is coated on the silicon particles, and then carbon nanotubes are attached to the surface, and then these materials are spherical. The surface of the silicon particles is covered with a carbon film, which is nanometer-scale (10-20 nm), and carbon nanotubes are adhered to the film. In this way, the carbon nanotubes are filled between the silicon particles, which not only serve as a conductive function, but also function to absorb the volume expansion of the silicon particles. Finally, these composite materials of silicon and carbon adhered to carbon nanotubes are spray-dried to form pellets of one particle. The diameter of these beads is about 10 microns. The composite particles under scanning electron microscope are as shown in the figure. 7 is shown.
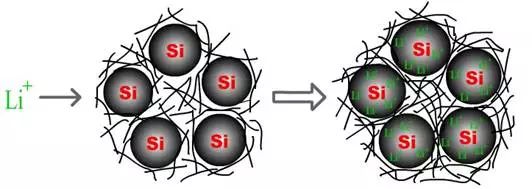
Figure 6. Ternary embedded composite structure

Figure 7. SEM of ternary embedded composite structure silicon carbon anode material
Four or three-element cladding structure
The Institute of Physics and Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a silicon-carbon composite material with a watermelon structure, as shown in Figure 8. The nano-silicon is doped with graphite composite, and then a layer of carbon material is wrapped on the outer layer to form a silicon-carbon composite material similar to the watermelon structure. The structure can effectively alleviate the volume change and particle fragmentation at the high density of the electrode. Based on practical considerations, the prepared silicon-carbon negative electrode has a suitable reversible capacity of 620 mA·h/g and exhibits cycle stability of more than 500 cycles at a high surface capacity (2.54 mA·h/cm 2 ). And excellent rate performance.
The preparation process of the silicon-carbon composite material includes a ball milling method, a high temperature cracking method, a chemical vapor deposition method, a sputtering deposition method, an evaporation method, and the like. Therefore, the silicon-carbon material structure is various, but it is designed with the idea of ​​increasing the capacity of the lithium battery and reducing the swelling and smashing of the silicon particles.
Regarding the market situation of silicon-carbon anodes, domestic anode material manufacturers such as Shanshan, Jiangxi Zijing, Shenzhen Beitui, etc. have already laid out the production of silicon-carbon anode materials, and several silicon-carbon anode materials have been introduced and have certain Capacity; some lithium-ion manufacturers in the market have adopted silicon-carbon composite materials as anode materials for lithium batteries. In domestic battery companies, Guoxuan Hi-Tech, BYD, CATL, Lishen, Wanxiang A123, Weihong Power, etc. The development and trial production of the carbon negative electrode system is underway; in foreign companies, Tesla uses a 10% silicon-based material in artificial graphite and a silicon-carbon negative electrode as a new power battery material on Model 3, with a battery capacity of 550 mAh. Above /g, the battery energy density can reach 300 wh/kg.
Japan's GS Yuasa Corporation has introduced a silicon-based anode material lithium battery, which has been successfully applied to Mitsubishi Motors. Hitachi Maxell has announced that it has developed a silicon battery with high current capacity. The production and utilization of silicon-carbon anodes are in full swing. It is believed that silicon-carbon anode materials will have a qualitative and quantitative leap in the lithium battery market in 2018.
Villa Lift,Attic Elevator,Small Lift For Home,Electric Lifts For Homes
XI'AN TYPICAL ELEVATOR CO., LTD , https://www.chinaxiantypical.com