In the field of intelligent driving sensors, compared with Lidar (LiDAR), Millimeter-Wave Radar is more grounded, technically mature, and its market shipments are considerable, taking the Chinese market as an example. In 2015, the sales volume of the vehicle's millimeter-wave radar was 1.8 million, and an average of one millimeter-wave radar was carried out for every 12 vehicles. In addition, the penetration rate of millimeter wave radars in Europe is very high.
First, the division of the millimeter wave band
The millimeter wave is essentially an electromagnetic wave. The frequency band of the millimeter wave is special, the frequency is higher than the radio, lower than the visible light and the infrared light, and the frequency is roughly in the range of 10 GHz to 200 GHz. The millimeter wave is between the microwave (Micro waves) and THz (1000 GHz), which can be said to be a subset of the microwave.
In this frequency band, the millimeter-wave related characteristics make it ideal for use in the automotive field. At present, there are three types of millimeter wave radar bands in the more common vehicle field.
The first one is the 24-24.25 GHz band, which is currently widely used in blind spot monitoring and lane change assistance for automobiles. The radar is installed in the rear bumper of the vehicle to monitor whether there is a car in the lanes on the rear sides of the vehicle and whether it can be changed. This band also has its shortcomings. First, the frequency is relatively low. In addition, the bandwidth (bandwidth) is relatively narrow, only 250MHz.
The other frequency band is 77 GHz. The frequency of this frequency band is relatively high, and the internationally allowed bandwidth is as high as 800 MHz. According to Yuan Shuai, the radar performance of this frequency band is better than that of the 24GHz radar, so it is mainly used to assemble on the front bumper of the vehicle, to detect the distance from the preceding vehicle and the speed of the preceding vehicle. The main realization is emergency braking and automatic. Follow the car and other active security areas.
The third type of application frequency band is 79GHz-81GHz. The biggest feature of this frequency band is that its bandwidth is very wide, which is more than 3 times higher than 77GHz, which also makes it have a very high resolution (Lei Feng network new wisdom driving: after The text will explain "resolution" in detail, which can reach 5cm. This resolution is very valuable in the field of autonomous driving, because autonomous vehicles have to distinguish between many fine objects such as pedestrians and have high bandwidth requirements. Yuan Shuai said that this band will have a wide range of applications in the future of autonomous driving.
In terms of wavelength, the wavelength of the 24 GHz millimeter wave is 1.25 cm, and the wavelength of the 77 GHz millimeter wave is about 4 mm, and the wavelength of the millimeter wave is more than 1000 times longer than the wavelength of the light wave, so that it has a stronger penetrating ability to an object.
For example, the diameter of dust we usually see is between 1um and 100um, and the diameter of natural raindrops is in the range of 0.5mm to 4mm. Therefore, electromagnetic waves with wavelengths equal to or longer can easily penetrate these obstacles, and millimeter waves have such capabilities.
This kind of reliability is difficult to achieve with any other sensor, so in the field of ADAS, which has high requirements on safety and reliability, the millimeter wave radar has a difficult position to shake.
Second, the development history of millimeter wave radar in the automotive field
In fact, in the United States in the 1960s, the millimeter-wave radar began to be used in the automotive field, but at that time the process level was low, the application was a single antenna, and the front end could only be received one at a time, and its frequency was only 10 GHz. Moreover, in Yuan Shuai’s description, this kind of radar device is not beautiful in front of the vehicle. “It’s basically like two dishes are there.â€
Later, in order to reduce its size, industry experts continue to raise the frequency to 30GHz, 50GHz. The higher the radar frequency, the smaller the antenna size, which means that the radar of the same size has a higher concentration of antenna beams.
In the 1990s, millimeter-wave radars of 60 GHz, 77 GHz, and 94 GHz were developed. The 60 GHz band was later mainly used for communication, 94 GHz was mainly used in the military band, and the industry chose 77 GHz as the band of the mainstream millimeter wave radar.
In history, there are also typical millimeter wave radar applications. In 1992, the US Department of Transportation installed 1,500 millimeter-wave radars on Greyhound buses. By 1993, it achieved immediate results: the traffic accident rate dropped by 25%. However, in the end, it was completely dismantled in 1994 because the effect was too good and damaged the interests of some vested interests.
Today, there are four major millimeter wave radar suppliers in the world (Lei Feng Wang Xinzhi: Of course, their business is not limited to millimeter wave radar), referred to as ABCD, namely Autoliv, Bosch, ConTInental and Delphi.
Autoliv is mainly based on 24GHz blind spot and lane change assisted radar. The main customer is Daimler Benz - its vehicles are basically equipped with lane change aids. Autoliv's millimeter wave radar has a large shipment.
Bosch's millimeter-wave radar is mainly 77 GHz, covering a wide range of faces, with long range (LRR), medium distance (MRR) and blind spot radar for rear of the car. Bosch's solution is very highly integrated, and the output is a control signal for the car. It is highly customizable and usually cooperates with a large car company to promote the project together.
ConTInental has both 24GHz and 77GHz in millimeter wave radar products, and its performance is not bad. Daimler's 77GHz millimeter wave radar is mainly supplied by ConTInental.
Delphi is an old American company, mainly based on 77GHz millimeter wave radar, using a more traditional hardware solution, the cost is relatively high, and the performance is good.
Third, millimeter wave radar detection of distance, speed and angle
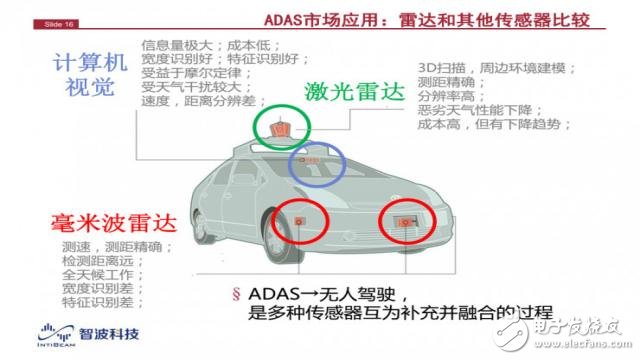
It is important to be clear that the performance exhibited by the millimeter-wave radar at the distance, speed and angle of the measurement target is slightly different from that of other sensors. The visual sensor obtains two-dimensional information without depth information, while the millimeter wave radar has depth information and can provide the target distance; the laser radar is not sensitive to speed, and the millimeter wave radar is very sensitive to speed and can be directly Get the speed of the target, because the millimeter wave radar will have a very obvious Doppler effect, and the speed of the target can be extracted by detecting its Doppler shift.
The most basic detection technique of millimeter wave radar is to use FMCW continuous chirp to detect the distance of the object in front. The millimeter wave radar emits continuous wave, which is larger than the laser radar in the back end processing.
The principle is:
The oscillator produces a signal that gradually increases in frequency over time. When the signal encounters an obstacle, it bounces back, with a delay of 2 times the distance/speed of light. There is a frequency difference between the returned waveform and the emitted waveform. This frequency difference and the delay are linear: the farther the object is, the later the returning wave is received, then the frequency difference between it and the incident wave. The value is greater.
By subtracting these two frequencies, the difference frequency (beat frequency) of the two frequencies can be obtained, and the distance of the obstacle can be judged by judging the level of the beat frequency.
In addition, in order to detect the speed of the target, there are also more advanced frequency modulation techniques, mainly based on the principle of Doppler shift.
Angle detection is achieved by the delay of receiving signals by multiple receiving antennas. For a simple example, suppose there are two antennas that receive electromagnetic waves emitted from a certain direction. The time that the electromagnetic waves reach the two antennas is different, or the phase difference. The phase difference can be used to evaluate the angle of the signal. .
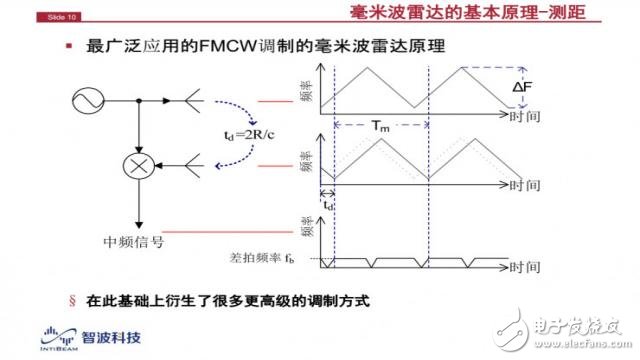
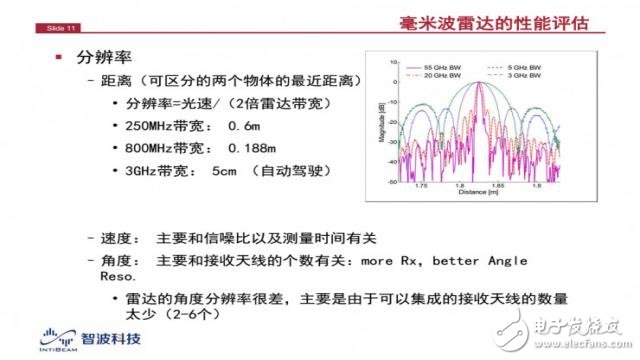
Here is a very important concept to be introduced - the resolution of millimeter wave radar. It is defined as "the closest distance between two objects that the radar can distinguish." For example, if two objects are close together, the radar may list them as an object. If they are separated, the radar will see two. object. So how far away from the radar can distinguish the distance between two objects, this is called the resolution of the radar.
The resolution calculation formula is also very simple, that is, the speed of the light is 2 times the radar bandwidth, so for 24GHz and 77GHz, the resolution can be directly calculated. The former is 0.6m and the latter is about 20cm. The 3GHz bandwidth millimeter wave radar has a resolution of 5cm, making it ideal for autonomous driving applications.
In addition, in terms of critical antenna technology, there are two types of millimeter-wave radar, one based on lenses and the other on PCB. Lens-based antenna development is less flexible because it will eventually focus on a small area that is not easily configurable for flexible design.
Fourth, the future
In general, the cost of millimeter wave radar is still falling faster because it is a silicon-based chip and there are no particularly expensive and complicated processes. The laser radar has high requirements in the transceiver and assembly process of light, and the cost is difficult to reduce.
A very important technology for Lidar is solid-state laser radar. It is actually in line with traditional radar and millimeter-wave radar. Solid-state laser radar is essentially adjusting the phase of each transmitting and receiving unit. The millimeter-wave radar is also the same. The principle is that the millimeter wave radar is operating on electromagnetic waves, and the implementation of the device is much more difficult than the phase change of the light band.
And for the market prospect of millimeter wave radar. A car will carry 3-8 millimeter-wave radars, and currently 7 cars have been installed on Mercedes-Benz's high-end cars. In the next 10 years, the market size of the vehicle's millimeter-wave radar will not be underestimated.
In terms of policy, each country is promoting the AEB function of automobiles, of which Japan and North America are already being implemented, and China will also be introduced to the commercial vehicle field in 2018.
Millimeter wave radar is a sensor that is difficult to replace in the field of ADAS. Although it has some shortcomings, it is the only sensor that works around the clock. The accuracy of its speed measurement and ranging is much higher than that of vision. Compared with laser radar, its speed measurement accuracy will be higher. Penetration will be better. But on the whole, this is not a conflict, because the future will move toward convergence, especially for unmanned driving, and there is no doubt that the three sensors will merge with each other.
| About Bare Copper Wire |
Good conductivity; Strong anticorrosion; Long service life; Lowest price; Easy installation
Bare Copper Wire is used as flexible connector in electric transmission and distribution appliance(such as volt transformer, electric
stove),electronic equipment and thyristor. Underground Electrical Wire also could be used for grounding wire in electric working.
Also, it can be manufactured accordingto customer's drawings and demands.

| 1. | Professional Operation Experience |
| 2. | The Sizes All Can Be Customised |
| 3. | Sample For Your Reference Available |
| 4. | Low MOQ, Low Price |
| 5. | Safe Packing & Prompt Delivery |
| 6. | Quality Guaranted: ISO9001:2008, All Kinds of Test |
Bare Copper Wire,Bare Copper Wire Solid,Copper Wire Bare Copper Wire,Pure Copper Wire Bare Copper
HENAN HUAYANG ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY GROUP CO.,LTD , https://www.huaonwire.com