According to the University of New South Wales and the National Laboratory of San Diego, the ethanol fuel stratification technology can significantly reduce the compression ratio of the HCCI engine and increase the engine's high load limit.
In the simulation experiment, the experimental team used the multi-space model combined with the factors of nitrogen oxide emissions to evaluate the effect of ethanol fuel stratification technology to reduce the HCCI engine pressurization rate.
The HCCI engine works like a spark-ignited diesel engine. Like diesel engines, throttling losses and high compression ratios result in extremely high thermal efficiencies. The fuel mixture is premixed to form a homogeneous mixture that is diluted in the cylinder. The combination of these factors, in addition to soot burning, produces very little harmful nitrogen oxides.
Although the HCCI engine has many advantages, it still has to overcome several difficulties. The first is the high compression at high loads that causes the engine to knock, which can damage the engine block. Secondly, unlike spark-ignition engines, which are limited by the flame propagation speed, and unlike diesel engines, which are limited by the mixed injection speed, the small oil droplets in the HCCI engine cylinder are burning at the same time. Fuel stratified injection technology may solve this problem.
The stratified injection of fuel can be realized by layered electrified compression ignition, including homogeneous compression ignition and two-stage ignition to control the fuel concentration at any time to achieve the purpose of reducing the compression ratio.
When the fuel is directly injected into the combustion chamber, local cooling is achieved by fuel stratified injection. Since the single-stage ignition is sensitive to temperature, if the fuel mixer temperature is high enough, the compression ratio can be reduced.
There is a trade-off between soot emissions and nitrogen oxides, which reduces oxide emissions, lowers temperatures, incomplete oxidation of soot, and increases emissions.
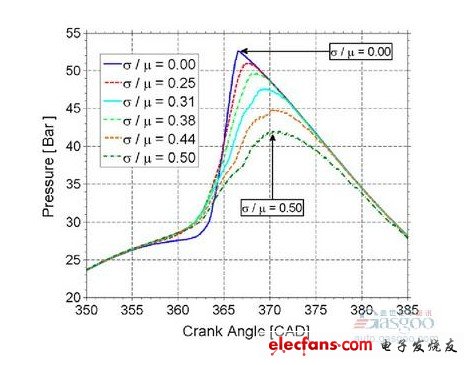
Ethanol is by far the best HCCI engine fuel. Because of the high boiling point of water, they also considered a mixture of water and ethanol.
They built a multi-space model and validated the natural stratification data for the HCCI engine, then extended the range to the fuel stratification model and calculated the fuel stratification evaporation in the simulation model. This leads to an increase in fuel stratification in the cylinder. research shows:
• The model accurately predicts the ignition timing of ethanol; it also predicts the compression ratio of thermal stratification. When the compression ratio is high, it does not cause delamination, and the stratification is continuously increased to cause the engine to stall.
Long-term combustion, coupled with varying amounts of evaporative cooling, exacerbates stratification. The intensified stratification has led to the continuation of combustion.
• Unlike two-stage ignition, lean ethanol mixed ignition emits very small amounts of nitrogen oxides.
A drawback of the fuel stratification technique is that a large amount of nitrogen oxides are generated when the local temperature is high, while the combustion efficiency is lowered when the temperature is too low. The mixed fuel after adding water can reduce the emission of nitrogen oxides and reduce the compression ratio. This will be a higher level of layering technology.
Aluminum Based Pcb,Aluminum Based Circuit Board,Electrical Circuit Board,Double-Sided Pcb Circuit Board
Shenzheng Weifu Circuit Technology Co.Ld , https://www.wfcircuit.com