Timing attacks can be used in security-protected password-based microcontrollers, or systems that use a definite digital card or password for access control, such as Dallas' iButton products. A common risk in these systems is that the consecutive numbers entered are verified again in the database.
First understand what the MCU is - structure and composition
I: CPU, including the operator, controller, and register bank. It is the core component inside the MCU and consists of two parts: the computing component and the control component. The former can complete the arithmetic logic operation of the data, the bit variable processing and the data transfer operation, and the latter is to coordinate the work at a certain timing, and is a component for analyzing and executing the instructions.
II: Memory, including ROM and RAM. ROM program memory, the work of the MCU is executed in a sequence according to the pre-programmed program. The ROM program memory is used to store the programmed program (the system program is compiled and written by the manufacturer). The stored data does not disappear after power down. The ROM is further divided into on-chip memory and off-chip (extended) memory.
III: Input and output I/O interfaces, connected to external input and output (circuit) devices. Digital I/O interface such as PO/P1/P2/P3, the internal circuit includes circuit such as port latch, output driver and input buffer. Among them, PO is a three-state bidirectional interface, P1/P2/P3 digital I/O port, and the internal driver is an “open collector†output circuit. When applied, internal or external circuits are connected with pull-up resistors. Each port can be used as a digital signal input or output port, and has a multiplexing function (refer to the port function has a first function, a second function or even several functions, which can be flexibly set in the application).
In addition to the digital I/O port, the MCU device also has an ADC analog input and output port. The input signal is converted into a digital (frequency) signal by an internal A/D conversion circuit, and then processed; for an analog signal, After D/A conversion, it is output to an external circuit.
Let's talk about how to crack the MCU method
First, non-intrusive attacks
There is no need to initialize the components. Components can be placed in the test circuit for analysis during attack, or components can be connected separately. Once successful, this type of attack is easy to popularize and there is no significant overhead in re-attacking. In addition, the use of this attack will not leave a trace. Therefore, this is considered to be the biggest threat to the hardware security of any component. At the same time, it usually takes a lot of time and effort to find a non-intrusive attack method for a particular component. This usually reverses the engineering of components, including disassembling software and understanding hardware layouts.
Non-intrusive attacks can be passive or active. Passive attacks, also known as side attacks, do not affect the component being attacked, but usually observe its signal and electromagnetic radiation. Such as power analysis and clock attack. Active attacks, such as exhaustive attacks and noisy attacks, feature adding signals to components, including power lines.
A simple non-intrusive attack can be to replicate an SRAM-based FPGA with a powered configuration. Connect the JATG interface for the configuration chip and capture all signals with an oscilloscope or logic analyzer. You can then analyze the waveform and reply to a unique command.
When only half of the FPGA resources are used, the fact that the data stream can be slightly changed to camouflage piracy can be used. Leave a little space in the configuration without affecting the operation of the components. The JTAG interface also has some freedom in transmitting signal timing, so the pirated waveform can be set to look different from the original signal. In addition, the cracker can exchange the row address when uploading, giving the impression that the design is completely different.
Vague and safe
Semiconductor manufacturers have provided major customers with measures to enhance product anti-cracking capabilities: customer printing on the packaging replaces standard chip models. This gives the impression that the product is designed by a custom integrated circuit. As we all know, ASIC provides good protection measures to prevent multiple attacks, and only a few experienced and well-equipped crackers can successfully crack. This will discourage many potential crackers. But a confident cracker will try to determine if the chip is really an ASIC in a simple way. The easiest way is to look at the pins that are connected to the power, ground, clock, reset, serial or other interface. This result is very reliable compared to suspected microcontrollers in the database, and each microcontroller has its own pin characteristics. Once the similarity is found, put it on the general purpose writer and try to read the result.
Another easy way is to restrict access to the program memory. Usually used in smart cards, but also used in some microcontrollers. This is not a very reliable and practical method. Of course, it is used very well in smart cards, and all customers are forced to sign non-proliferation agreements with chip manufacturers. But microcontrollers are rare, and many microcontrollers that can be programmed by general-purpose programmers are available in the world. Even if there are no programming specifications in the file, you can use the low-cost oscilloscope to take out the required waveforms in a few hours. If the microcontroller is not supported by a special general purpose writer, a direct and complete protocol can still be obtained by purchasing a development board from the manufacturer.
Second, timing attacks (TIming attacks)
Some safety-related operations use input values ​​and keys that are compared by semiconductor chips for different times. Careful timing measurements and analysis can recover the key. This method was first mentioned in the 1996 literature. Later, this attack successfully cracked the actual RSA-signed smart card.
In order for the attack to succeed, information about the device needs to be collected, compared to the processing time integration, such as the quesTIon-answer delay. Many cryptographic algorithms are susceptible to timing attacks, the main reason being software to execute algorithms. That includes performing branches and operating conditions that are needed to skip at the right time; using caching; not fixing time processing instructions such as multipliers and crossovers; and a host of other reasons. The result is that execution capabilities typically depend on the key and the input data.
First understand what the MCU is - structure and composition
I: CPU, including the operator, controller, and register bank. It is the core component inside the MCU and consists of two parts: the computing component and the control component. The former can complete the arithmetic logic operation of the data, the bit variable processing and the data transfer operation, and the latter is to coordinate the work at a certain timing, and is a component for analyzing and executing the instructions.
II: Memory, including ROM and RAM. ROM program memory, the work of the MCU is executed in a sequence according to the pre-programmed program. The ROM program memory is used to store the programmed program (the system program is compiled and written by the manufacturer). The stored data does not disappear after power down. The ROM is further divided into on-chip memory and off-chip (extended) memory.
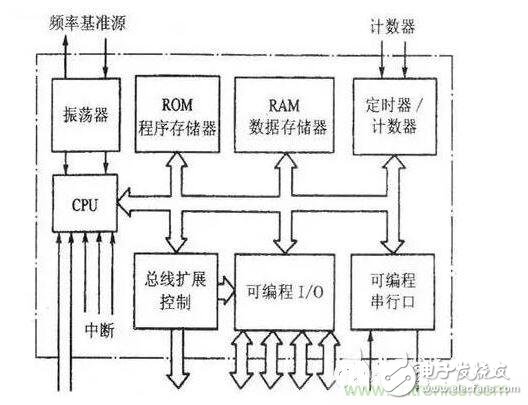
III: Input and output I/O interfaces, connected to external input and output (circuit) devices. Digital I/O interface such as PO/P1/P2/P3, the internal circuit includes circuit such as port latch, output driver and input buffer. Among them, PO is a three-state bidirectional interface, P1/P2/P3 digital I/O port, and the internal driver is an “open collector†output circuit. When applied, internal or external circuits are connected with pull-up resistors. Each port can be used as a digital signal input or output port, and has a multiplexing function (refer to the port function has a first function, a second function or even several functions, which can be flexibly set in the application).
In addition to the digital I/O port, the MCU device also has an ADC analog input and output port. The input signal is converted into a digital (frequency) signal by an internal A/D conversion circuit, and then processed; for an analog signal, After D/A conversion, it is output to an external circuit.
Let's talk about how to crack the MCU method
First, non-intrusive attacks
There is no need to initialize the components. Components can be placed in the test circuit for analysis during attack, or components can be connected separately. Once successful, this type of attack is easy to popularize and there is no significant overhead in re-attacking. In addition, the use of this attack will not leave a trace. Therefore, this is considered to be the biggest threat to the hardware security of any component. At the same time, it usually takes a lot of time and effort to find a non-intrusive attack method for a particular component. This usually reverses the engineering of components, including disassembling software and understanding hardware layouts.
Non-intrusive attacks can be passive or active. Passive attacks, also known as side attacks, do not affect the component being attacked, but usually observe its signal and electromagnetic radiation. Such as power analysis and clock attack. Active attacks, such as exhaustive attacks and noisy attacks, feature adding signals to components, including power lines.
A simple non-intrusive attack can be to replicate an SRAM-based FPGA with a powered configuration. Connect the JATG interface for the configuration chip and capture all signals with an oscilloscope or logic analyzer. You can then analyze the waveform and reply to a unique command.
When only half of the FPGA resources are used, the fact that the data stream can be slightly changed to camouflage piracy can be used. Leave a little space in the configuration without affecting the operation of the components. The JTAG interface also has some freedom in transmitting signal timing, so the pirated waveform can be set to look different from the original signal. In addition, the cracker can exchange the row address when uploading, giving the impression that the design is completely different.
Vague and safe
Semiconductor manufacturers have provided major customers with measures to enhance product anti-cracking capabilities: customer printing on the packaging replaces standard chip models. This gives the impression that the product is designed by a custom integrated circuit. As we all know, ASIC provides good protection measures to prevent multiple attacks, and only a few experienced and well-equipped crackers can successfully crack. This will discourage many potential crackers. But a confident cracker will try to determine if the chip is really an ASIC in a simple way. The easiest way is to look at the pins that are connected to the power, ground, clock, reset, serial or other interface. This result is very reliable compared to suspected microcontrollers in the database, and each microcontroller has its own pin characteristics. Once the similarity is found, put it on the general purpose writer and try to read the result.
Another easy way is to restrict access to the program memory. Usually used in smart cards, but also used in some microcontrollers. This is not a very reliable and practical method. Of course, it is used very well in smart cards, and all customers are forced to sign non-proliferation agreements with chip manufacturers. But microcontrollers are rare, and many microcontrollers that can be programmed by general-purpose programmers are available in the world. Even if there are no programming specifications in the file, you can use the low-cost oscilloscope to take out the required waveforms in a few hours. If the microcontroller is not supported by a special general purpose writer, a direct and complete protocol can still be obtained by purchasing a development board from the manufacturer.
Second, timing attacks (TIming attacks)
Some safety-related operations use input values ​​and keys that are compared by semiconductor chips for different times. Careful timing measurements and analysis can recover the key. This method was first mentioned in the 1996 literature. Later, this attack successfully cracked the actual RSA-signed smart card.
In order for the attack to succeed, information about the device needs to be collected, compared to the processing time integration, such as the quesTIon-answer delay. Many cryptographic algorithms are susceptible to timing attacks, the main reason being software to execute algorithms. That includes performing branches and operating conditions that are needed to skip at the right time; using caching; not fixing time processing instructions such as multipliers and crossovers; and a host of other reasons. The result is that execution capabilities typically depend on the key and the input data.
Control Cable,Control Wire,Shielded Control Cable,Power Control Cable
HENAN QIFAN ELECTRIC CO., LTD. , https://www.hnqifancable.com