Abstract: Different manufacturers provide quartz crystals of various shapes and sizes, and their performance indicators are also different. These indicators include resonance frequency, resonance mode, load capacitance, series impedance, case capacitance, and drive level. This application note helps the reader understand these specifications and allows the user to select the appropriate crystal according to the application and obtain the best results in the MAX1470 superheterodyne receiver circuit application.
Different manufacturers provide quartz crystals of various shapes and sizes, and their performance indicators are also different. These indicators include resonance frequency, resonance mode, load capacitance, series impedance, case capacitance, and drive level. This application note helps readers understand these specifications and allows users to choose the right crystal according to the application and obtain the best results in the MAX1470 superheterodyne receiver circuit application.
The equivalent circuit of the crystal is shown in Figure 1. The figure includes dynamic components: resistance Rs, inductance Lm, capacitance Cm and parallel capacitance Co. These dynamic components determine the crystal's series resonance frequency and the Q value of the resonator. The parallel capacitance Co is the result of the action of the crystal electrode, shell and leg.
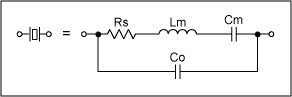
Figure 1. Crystal model
The main performance indicators are given in detail below. Resonance frequency The crystal frequency can be specified according to the reception frequency. Since the MAX1470 uses a low-end injected 10.7MHz intermediate frequency, the crystal frequency can be given by the following formula (in MHz):
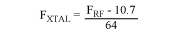
For 315MHz applications, the frequency of the crystal can be 4.7547MHz, while in 433.92MHz applications, a 6.6128MHz crystal is required. Only crystals in fundamental frequency mode need to be specified (no overtone required). Resonance mode crystals have two resonance modes: series (low frequency of two frequencies) and parallel (anti-resonance, high frequency of two frequencies). All crystals exhibiting pure resistance in the oscillation circuit exhibit two resonance modes. In the series resonance mode, the capacitive reactance Cm and the inductive reactance Lm of the dynamic capacitor are equal and opposite, and the impedance is minimum. At the anti-resonance point. The impedance is the largest, and the current is the smallest. Anti-resonance points are not used in oscillator applications.
By adding external components (usually capacitors), the quartz crystal can oscillate at any frequency between the series and anti-resonant frequencies. In the crystal industry, this is the parallel frequency or parallel mode. This frequency is higher than the series resonance frequency and lower than the true parallel resonance frequency (anti-resonance point) of the crystal. Figure 2 shows the characteristic graph of the typical crystal impedance versus frequency.

Figure 2. Crystal impedance vs. frequency load capacitance and traction. Load capacitance is an important indicator of the crystal when using the parallel resonance mode. In this mode, the total reactance of the crystal is inductive and is connected in parallel with the load capacitance of the oscillator to form an LC resonant circuit, which determines the frequency of the oscillator. When the load capacitance value changes, the output frequency also changes accordingly. Therefore, the crystal manufacturer must know the load capacitance in the oscillator circuit so that the same load capacitance can be used in the factory for calibration.
If a crystal resonating on a different load capacitor is used, the crystal frequency will deviate from the rated operating frequency, so that the reference frequency will introduce errors. Therefore, an external capacitor needs to be added to change the load capacitance, so that the crystal oscillates to the required operating frequency again.
Figure 3 shows the crystal diagram in the MAX1470 EV kit circuit. In this circuit, C14 and C15 are series traction capacitors, and C16 is a parallel traction capacitor. Cevkit is the equivalent MAX1470 chip plus the parasitic capacitance of the evaluation PCB. Cevkit is about 5pF.
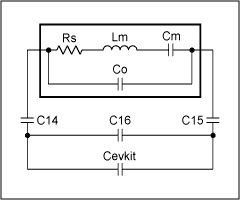
Figure 3. Evaluation board crystal equivalent circuit
Series traction capacitors will speed up the crystal oscillation, while parallel capacitors will slow down the oscillation. Cevkit is 5pF, if you use a crystal with a load capacitance of 5pF, it will oscillate to the required frequency, so no external capacitor is required (C16 is not connected, and C14 and C15 are shorted on the board). The evaluation board itself uses a crystal with a 3pF load capacitor and requires two 15pF capacitors in series to accelerate oscillation. The calculation of the load capacitance is as follows:

In this example, if two series capacitors are not used, the 4.7547MHz crystal will oscillate at 4.7544MHz, and the receiver will be tuned to 314.98MHz instead of 315.0MHz, with a frequency error of about 20kHz, which is 60ppm.
Therefore, the key is to use series or parallel or two forms to match the load capacitance of the crystal (depending on the value of the capacitor). For example, a 1pF parallel capacitor is required for a 6pF load capacitor (or a combination of the following: C14 = C15 = 27pF, C16 = 5pF).
Use C16 with a large capacitance value cautiously, because it will increase the current of the resonant circuit and cause the crystal to stop oscillation. Figure 4 shows the relationship between the parallel capacitance and the oscillator current.

Figure 4. Relationship between crystal oscillator current and additional parallel load capacitance
In a customized PCB board, if Cevkit is unknown, you can use a spectrum analyzer to monitor the intermediate frequency (be sure to use a DC blocking capacitor before the signal enters the spectrum analyzer), and then use series and parallel capacitors to tune the intermediate frequency to 10.7MHz. Series resistance The typical series resistance of an ordinary crystal is 25Ω to 100Ω. Crystal manufacturers usually give the characteristics of this resistor and specify its maximum value. In the MAX1470 oscillator circuit, the resistance should not exceed 100Ω. The case or parallel capacitor is the capacitance of the crystal electrode, case and pin. Typical values ​​range from 2pF to 7pF. The driving level must limit the power consumption of the crystal, and the quartz crystal will stop vibrating under the condition of excessive mechanical vibration. Due to the non-linearity, the crystal characteristics also change with the drive level. The crystal manufacturer will specify the maximum drive level according to the special production line. Use a crystal with a drive level in the range of 1µW.
These performance indicators can guide users to choose the right crystal to meet the needs of the MAX1470 oscillator circuit, and can improve the overall performance of the receiver.
Different manufacturers provide quartz crystals of various shapes and sizes, and their performance indicators are also different. These indicators include resonance frequency, resonance mode, load capacitance, series impedance, case capacitance, and drive level. This application note helps readers understand these specifications and allows users to choose the right crystal according to the application and obtain the best results in the MAX1470 superheterodyne receiver circuit application.
The equivalent circuit of the crystal is shown in Figure 1. The figure includes dynamic components: resistance Rs, inductance Lm, capacitance Cm and parallel capacitance Co. These dynamic components determine the crystal's series resonance frequency and the Q value of the resonator. The parallel capacitance Co is the result of the action of the crystal electrode, shell and leg.

Figure 1. Crystal model
The main performance indicators are given in detail below. Resonance frequency The crystal frequency can be specified according to the reception frequency. Since the MAX1470 uses a low-end injected 10.7MHz intermediate frequency, the crystal frequency can be given by the following formula (in MHz):
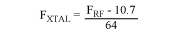
For 315MHz applications, the frequency of the crystal can be 4.7547MHz, while in 433.92MHz applications, a 6.6128MHz crystal is required. Only crystals in fundamental frequency mode need to be specified (no overtone required). Resonance mode crystals have two resonance modes: series (low frequency of two frequencies) and parallel (anti-resonance, high frequency of two frequencies). All crystals exhibiting pure resistance in the oscillation circuit exhibit two resonance modes. In the series resonance mode, the capacitive reactance Cm and the inductive reactance Lm of the dynamic capacitor are equal and opposite, and the impedance is minimum. At the anti-resonance point. The impedance is the largest, and the current is the smallest. Anti-resonance points are not used in oscillator applications.
By adding external components (usually capacitors), the quartz crystal can oscillate at any frequency between the series and anti-resonant frequencies. In the crystal industry, this is the parallel frequency or parallel mode. This frequency is higher than the series resonance frequency and lower than the true parallel resonance frequency (anti-resonance point) of the crystal. Figure 2 shows the characteristic graph of the typical crystal impedance versus frequency.

Figure 2. Crystal impedance vs. frequency load capacitance and traction. Load capacitance is an important indicator of the crystal when using the parallel resonance mode. In this mode, the total reactance of the crystal is inductive and is connected in parallel with the load capacitance of the oscillator to form an LC resonant circuit, which determines the frequency of the oscillator. When the load capacitance value changes, the output frequency also changes accordingly. Therefore, the crystal manufacturer must know the load capacitance in the oscillator circuit so that the same load capacitance can be used in the factory for calibration.
If a crystal resonating on a different load capacitor is used, the crystal frequency will deviate from the rated operating frequency, so that the reference frequency will introduce errors. Therefore, an external capacitor needs to be added to change the load capacitance, so that the crystal oscillates to the required operating frequency again.
Figure 3 shows the crystal diagram in the MAX1470 EV kit circuit. In this circuit, C14 and C15 are series traction capacitors, and C16 is a parallel traction capacitor. Cevkit is the equivalent MAX1470 chip plus the parasitic capacitance of the evaluation PCB. Cevkit is about 5pF.

Figure 3. Evaluation board crystal equivalent circuit
Series traction capacitors will speed up the crystal oscillation, while parallel capacitors will slow down the oscillation. Cevkit is 5pF, if you use a crystal with a load capacitance of 5pF, it will oscillate to the required frequency, so no external capacitor is required (C16 is not connected, and C14 and C15 are shorted on the board). The evaluation board itself uses a crystal with a 3pF load capacitor and requires two 15pF capacitors in series to accelerate oscillation. The calculation of the load capacitance is as follows:

In this example, if two series capacitors are not used, the 4.7547MHz crystal will oscillate at 4.7544MHz, and the receiver will be tuned to 314.98MHz instead of 315.0MHz, with a frequency error of about 20kHz, which is 60ppm.
Therefore, the key is to use series or parallel or two forms to match the load capacitance of the crystal (depending on the value of the capacitor). For example, a 1pF parallel capacitor is required for a 6pF load capacitor (or a combination of the following: C14 = C15 = 27pF, C16 = 5pF).
Use C16 with a large capacitance value cautiously, because it will increase the current of the resonant circuit and cause the crystal to stop oscillation. Figure 4 shows the relationship between the parallel capacitance and the oscillator current.

Figure 4. Relationship between crystal oscillator current and additional parallel load capacitance
In a customized PCB board, if Cevkit is unknown, you can use a spectrum analyzer to monitor the intermediate frequency (be sure to use a DC blocking capacitor before the signal enters the spectrum analyzer), and then use series and parallel capacitors to tune the intermediate frequency to 10.7MHz. Series resistance The typical series resistance of an ordinary crystal is 25Ω to 100Ω. Crystal manufacturers usually give the characteristics of this resistor and specify its maximum value. In the MAX1470 oscillator circuit, the resistance should not exceed 100Ω. The case or parallel capacitor is the capacitance of the crystal electrode, case and pin. Typical values ​​range from 2pF to 7pF. The driving level must limit the power consumption of the crystal, and the quartz crystal will stop vibrating under the condition of excessive mechanical vibration. Due to the non-linearity, the crystal characteristics also change with the drive level. The crystal manufacturer will specify the maximum drive level according to the special production line. Use a crystal with a drive level in the range of 1µW.
These performance indicators can guide users to choose the right crystal to meet the needs of the MAX1470 oscillator circuit, and can improve the overall performance of the receiver.
LED power supply, CCTV center power supply device, LCD display power supply.
We can meet your specific requirement of the products, like label design. The plug type is US/UK/AU/EU. The material of this product is PC+ABS. All condition of our product is 100% brand new. OEM and ODM are available in our company, and you deserve the best service. You can send more details of this product, so that we can offer best service to you!
Power Supply,5V Power Supply,12V Power Supply, 24V Power Supply
Shenzhen Waweis Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.szwaweischarger.com