Definition of GPS positioning system
This article refers to the address: http://
The GPS positioning system refers to a system that uses satellites to locate and navigate in real time on a global scale, referred to as GPS (Global Positioning System). The GPS positioning system function must have three elements: GPS terminal, transmission network and monitoring platform; these three elements are indispensable; through these three elements, it can provide functions such as vehicle anti-theft, anti-robbery, driving route monitoring and call command.
The GPS positioning system is the second generation satellite navigation system in the United States. It was developed on the basis of the Meridian satellite navigation system, which adopted the successful experience of the Meridian system. Like the Meridian system, the GPS positioning system consists of three parts: the space part, the ground monitoring part and the user receiver.
The composition of the GPS positioning system
Space part (space part)
The space part of the GPS positioning system is composed of 24 GPS working satellites. These GPS working satellites form a constellation of GPS satellites, 21 of which are satellites for navigation and 3 are active satellites. The 24 satellites are orbiting the Earth on six orbits with an inclination of 55°. The satellite's operating period is about 12 stars. Each GPS working satellite emits a signal for navigation and positioning. GPS users use these signals to work. It can be seen that the role of the satellite part of the GPS positioning system is to continuously transmit navigation messages.
Control section
The control part of the GPS positioning system consists of a monitoring system consisting of several tracking stations distributed around the world. According to their functions, these tracking stations are divided into main control stations, monitoring stations and injection stations. The function of the master station is to calculate the satellite ephemeris and the correction parameters of the satellite clock based on the GPS observation data of each monitoring station, and inject the data into the satellite through the injection station; meanwhile, it also performs the satellite Control, issue instructions to the satellite, when the working satellite fails, dispatch the standby satellite to replace the failed working satellite; in addition, the main control station also has the function of the monitoring station. The monitoring station is equipped with a GPS user receiver, an atomic clock, sensors for collecting local meteorological data, and a computer for preliminary processing of data. The main task of the monitoring station is to obtain satellite observation data and transmit it to the master station. The role of the injection station is to inject the satellite ephemeris calculated by the master station and the correction number of the satellite clock into the satellite. This injection is performed once a day for each GPS satellite and for the final injection before the satellite leaves the range of the injection station.
User part (ground reception)
The user part of the GPS positioning system consists of a GPS receiver, data processing software and corresponding user equipment such as computer meteorological instruments. Its role is to receive signals from GPS satellites and use these signals for navigation and positioning.
These three parts together constitute a complete GPS positioning system.

GPS positioning system features
The GPS positioning system has the characteristics of good performance, high precision and wide application, and is the best navigation and positioning system to date. With the continuous improvement of the global positioning system, the continuous improvement of hardware and software, the application field is constantly expanding. Now it has spread to various sectors of the national economy and has begun to gradually deepen people's daily lives.
Principle of GPS positioning system
The basic principle of the GPS positioning system is to determine the position of the point to be measured according to the instantaneous position of the satellite moving at high speed as the known starting data and the method of spatial distance resection. As shown in the figure, it is assumed that the GPS receiver is placed on the ground to be measured at time t, and the time Δt at which the GPS signal arrives at the receiver can be determined. Together with other data such as the satellite ephemeris received by the receiver, the following four can be determined. Equations:
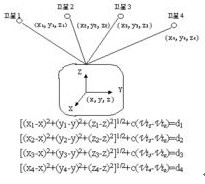
The coordinates x, y, z and Vto of the points to be measured in the above four equations are unknown parameters, where di = c Δti (i = 1, 2, 3, 4).
Di (i = 1, 2, 3, 4) is the distance between satellite 1, satellite 2, satellite 3, satellite 4 and the receiver, respectively.
Δti (i=1, 2, 3, 4) are the times that the signals of satellite 1, satellite 2, satellite 3, and satellite 4 arrive at the receiver, respectively.
c is the propagation speed of the GPS signal (ie, the speed of light).
The meaning of each parameter in the four equations is as follows:
X, y, and z are spatial rectangular coordinates of the coordinates of the point to be measured.
Xi, yi, zi (i = 1, 2, 3, 4) are space rectangular coordinates of satellite 1, satellite 2, satellite 3, and satellite 4 at time t,
It can be obtained from satellite navigation messages.
Vt i (i = 1, 2, 3, 4) is the clock difference of the satellite clocks of satellite 1, satellite 2, satellite 3, and satellite 4, respectively, provided by the satellite ephemeris.
Vto is the clock difference of the receiver.
From the above four equations, the coordinates x, y, z of the point to be measured and the clock difference Vto of the receiver can be solved.
Relativity provides the required corrections for GPS
GPS positioning system satellite timing signals provide information on latitude, longitude and altitude, and accurate distance measurements require precise clocking. Therefore, the exact GPS receiver will use the relativistic effect.
A GPS receiver with an accuracy of 30 meters means that it has taken advantage of the relativistic effect. Clifford M. Will, a physicist at the University of Washington, explained in detail: "If you don't consider the relativistic effect, the clock on the satellite is not synchronized with the clock of the Earth." The theory of relativity states that fast moving objects are slower than static over time. Will calculated that each GPS satellite spans about 14,000 kilometers per hour, which means that its on-board atomic clock is 7 microseconds slower per day than the Earth's clock.
Gravitation exerts a greater relativistic effect on time. At an altitude of about 20,000 kilometers, the GPS satellite receives a gravitational pull that is about a quarter of the ground. The result is that the onboard clock is 45 microseconds per day, and the GPS counts a total of 38 microseconds. Ashby explained: "If there is no frequency compensation on the satellite, it will increase the error by 11 kilometers per day." (This effect is actually more complicated because the satellite is along an eccentric orbit, sometimes closer to the Earth, sometimes Far away.
to sum up
This paper mainly introduces the concept, composition, principle and characteristics of GPS positioning system and the required corrections provided by the application of relativity in GPS positioning system.
Butt Connector,Lugs Insulated Female Connectors,Insulated Female Connectors,Non-Insulated Spade Terminals Wire Connector
Taixing Longyi Terminals Co.,Ltd. , https://www.longyiterminals.com