Transient change of voltage
The transient change of voltage, referred to as transient, refers to the instantaneous response of an electrical system when certain parameters change or external interference signals are generated. It mainly includes three characteristics: ultra high pressure, transient state, high frequency. According to its performance, it can be divided into the following three types:
Shock transient: A transient voltage wave propagating along a line or circuit, characterized by a slow rise after a rapid rise in voltage;
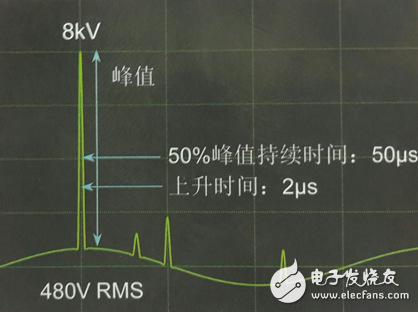
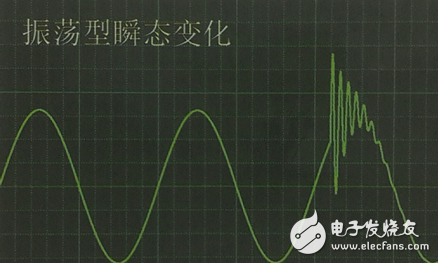
Oscillation transient: sudden change of signal voltage or current in steady state, and oscillate according to the natural frequency of the system; it will make the power signal alternately zoom in and out at a very fast speed, and often decay to zero in one cycle;
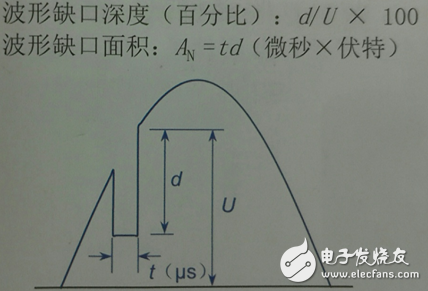
Voltage waveform notch: continuous (per cycle) voltage transients, such as distortion of the supply voltage waveform caused by a short phase-to-phase short circuit in a large converter during commutation.
Transient overvoltage
Voltage transients will cause a short-term effect on the operating circuit that is much higher than the operating voltage, ie transient overvoltage. The causes can be broadly divided into two categories:
External overvoltage: mainly caused by lightning strikes. It is characterized by short duration and strong impact. It is directly related to lightning activity and has nothing to do with the voltage level of the equipment.

Internal overvoltage: relative ground or phase transient overvoltage caused by line fault, no-load line switching, isolation switch operation of no-load bus, operation of no-load transformer or other causes in the system. Short time, unipolar or oscillating, strong attenuation voltage characteristics.

Transient overvoltage hazard
Hazard to capacitive load equipment: Any two conductors that are insulated and closely spaced from each other can form a capacitor. However, the insulation is only relative. Excessive voltage will cause the originally insulated object to conduct electricity (the capacitor is broken down), forming a small resistor, causing the current in the circuit to increase, burning the equipment in the circuit, and possibly even causing a fire. danger.

Hazard to inductive load devices: The solenoid has the characteristic of suppressing changes in the current applied to it. When the coil power supply is disconnected, in order to maintain the original current, a strong induced electromotive force (usually tens of times the applied voltage) can be generated, which not only causes strong interference to the circuit, but also electromagnetic induction. The disturbance is applied to the adjacent circuit to increase the insulation impact on the electrical products and the wear of the contacts.

Transient overvoltage measurement
In order to be able to monitor, capture and record voltage transients, power quality measuring instruments are required to have the following properties:
High sampling rate: steady state above 10kHz, transient above MHz
High dynamic range: input signal from several hundred volts to 8kV, instantaneous change more than 20 times
At the same time, IEC 61000-4-30 defines the measurement method for transients:
Envelope method: Set the waveform envelope range based on a sine wave as a starting condition for transient recording. It can be used for monitoring transients such as surges and waveform notches.
The rms method: using very fast sampling, calculated over an interval far less than one fundamental period, comparing the square root value to a set threshold.
Peak detection method: Set a fixed absolute threshold. When the voltage instantaneous value exceeds this value, it is a transient and can be used for surge monitoring.
Rolling window method: The instantaneous value is compared with the corresponding value in the previous cycle, which can be used to monitor the low frequency transient phenomenon of the power factor correction capacitor switching.
The fiber cutter is used to cut fiber as thin as hair. After hundreds of times of amplification, the cut fiber is observed to be flat before discharging the fuse.
The material of fiber is quartz, so the material of fiber cutting knife blade is required.
Adaptive fiber: single or multi-core quartz naked fiber;
Suitable for fiber cladding :100-250um diameter.

Fiber Optic Cleaver, Optical Fiber Cleaver, Fiber Optic Cutter, Hardware Networking Tools
NINGBO YULIANG TELECOM MUNICATIONS EQUIPMENT CO.,LTD. , https://www.yltelecom.com