Blue light hazard is a kind of photobiological hazard. The content of photobiosafety research is the interaction between light radiation and biological organisms. Optical radiation is defined as electromagnetic radiation having a wavelength of from 100 nm to 1 mm. However, since air has a strong absorption of light below 200 nm, and the light energy of less than 3000 nm is too negligible to the human body, the optical radiation range generally considered is 200-3000 nm.
First, the composition of white LED
A white LED is a white light emitting diode. White light is superimposed by a plurality of different wavelengths of light, and a white LED is an LED that can be used for general illumination.
Since it can get daylight color from the LED, it can be used for illumination. The mixing of light of a plurality of colors into white light can be obtained by various methods, and mixing of light of three colors is a common method. There are two main methods for obtaining white light with a gallium nitride-based LED: one is a combination of a blue LED and a YAG yellow phosphor (see Figure 1); the other is a red/green/blue (RGB) tri-color LED. The combination (see Figure 2).

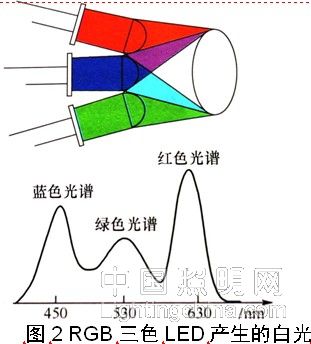
In order to obtain stable, reliable and simple white light, the most common method is to use a blue-emitting LED chip to excite the phosphor. The LED emits blue light with a wavelength of about 450 nm. In this process, the blue light is divided into two parts, a part of which is blue light. The phosphor is excited to emit yellow-green light with a wavelength of about 570 nm, and the other portion of the blue light is transmitted to mix with the yellow-green light generated by the excited phosphor to produce white light.
White light LED colorimetric parameters mainly have color temperature and color rendering. According to the proportion and composition of the phosphor, the white LED can provide a full range of color temperature range of 2700K~6500K with cool white, neutral and warm white. Color rendering is another important indicator of white LEDs as a general illumination source. Indoor lighting white LEDs require a color rendering index of 80 or higher.
One energy efficiency indicator of white LEDs is light efficiency, which is the ratio of the luminous flux emitted by the light source to the electrical power consumed by itself, in lm/W.
High color temperature LED white light is also called rich blue white light, rich in blue light. High light efficiency. Low color temperature LED white light, because most of the blue light has been converted into longer wavelength yellow green light and red light, so the light effect is lower.
Second, the basic concept of photobiosafety
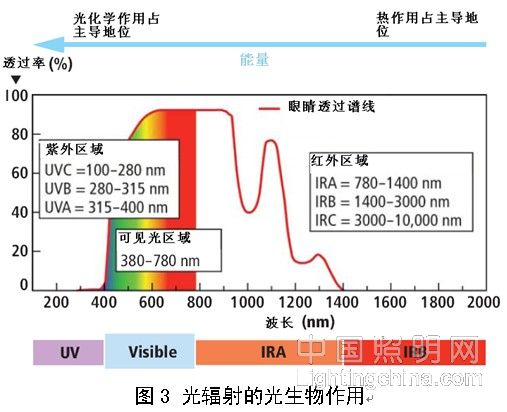
Since light radiation is absorbed by human tissue and can penetrate to a certain depth (UV penetration depth is several micrometers, and infrared penetration depth is several millimeters), human skin and eyes are exposed to light radiation. Below. The biological reaction of exposure to radiation is caused by a variety of energy transfer processes, and can generally be roughly divided into photochemical action and thermal action. Since the photon energy in the short-wave region is the highest, the photochemical reaction plays a major role in the short-wave region, while in the long-wave region, the thermal action dominates (see Figure 3).
1. Photochemical mechanism
In photochemical action, some specific wavelengths of light excite electrons in the cell's molecules, causing the breaking and recombination of chemical bonds in that region. This may have a direct effect on the double-stranded DNA, which may cause DNA damage and, in addition, produce highly reactive groups. These groups will react with DNA to cause structural reorganization, or react with photoreceptor cells such as the retina to cause a decrease in cell function or necrosis. It is important that damage to DNA can lead to cancer if it cannot be repaired.
2. Thermal mechanism
The mechanism of the thermal reaction is because some parts absorb light, causing the local temperature to rise. This will result in protein denaturation or cellular thermal damage.
3. Differences between photochemical action and thermal action mechanism
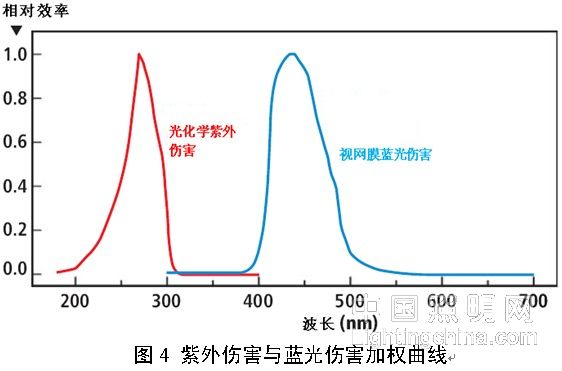
Thermal damage is consistent across the entire band, while photochemical damage is strongly dependent on wavelength. This property is represented by the damage weighting function (see Figure 4), which takes a certain wavelength to cause a certain dose of response. The reciprocal of (or energy) is eventually normalized.