High-precision, high-side current sensing is required for many applications such as motor control, solenoid control, and power management (such as DC-DC converters and battery monitoring). In this application, monitoring the high-side current rather than the loop current can improve diagnostic capabilities, such as determining short-circuit current to ground and continuously monitoring the return diode current, avoiding the use of sampling resistors and maintaining ground integrity. Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3 show typical high-side current sampling configurations for solenoid valve control and motor control, respectively.

Figure 1. High-end detection in typical solenoid valve control

Figure 2. High-end detection in a typical H-bridge motor control
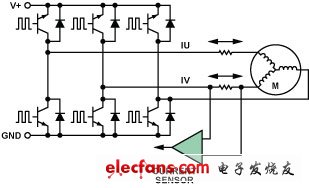
Figure 3. High-end detection in typical three-phase motor control
In all of the above configurations, the pulse width modulated (PWM) common mode voltage on the sampling resistor that monitors the load current oscillates from ground to power. The period, frequency, and rise/fall times of this PWM input signal can be determined using control signals from the power stage to the FET. Therefore, the differential measurement circuit that monitors the voltage across the sampling resistor requires extremely high common-mode voltage rejection and high-voltage processing capability, as well as high gain, high precision, and low offset—the purpose is to reflect the true load current value.
In solenoid valve control (Figure 1) using a single control FET, the current always flows in the same direction, so a unidirectional current detector is sufficient. In the motor control configuration (Figures 2 and 3), shunting the motor phase means that the current in the sampling resistor flows in both directions, thus requiring a bidirectional current detector.
Many semiconductor vendors offer a variety of solutions for high-end current sensing, and then design engineers working on such applications have found that they can be categorized by two distinct high-voltage structures: current-sense amplifiers and differential amplifiers.
Next, we'll detail the important differences between the two architectures to help high-end current-sensing design engineers choose the device that best fits their application. We will compare two high voltage devices: the AD8206 bidirectional differential amplifier and the AD8210 bidirectional current sense amplifier. Both devices have the same pins and feature high-side current-sampling monitoring, but their performance specifications and architecture are different. So how do you choose the right device?
Weighing Scale,Weighing Machine,Body Weight Scale,Weight Measuring Machine
GALOCE (XI'AN) M&C TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. , https://www.galoce-meas.com