The deadlines for major wireless operators and their suppliers to deploy 4G upgrade services and true 5G services are only a few months away. Almost all of them are working hard to meet their deadlines, so it is understandable that they have not had as much time to promote their 5G marketing/public relations activities in recent weeks as they did in previous years. Their work mainly involves testing, trials and new products, as well as preparing the spectrum for future services. Coincidentally, in the three largest countries in North America, major regulatory news has emerged.
Recently, the United States Federal Communications Commission (FCC) passed some regulations on the use of the 24GHz spectrum. Although these regulations are obscure, they still have important implications.
Until recently, only part of the 24GHz spectrum could be converted to 5G, because a large part of this frequency band has been used by radar. Due to technical reasons, the radar is shifting to 77GHz (see "Moving from 24 GHz to 77 GHz radar"). This transfer should be gradual, but eventually there will be more 24GHz bands available for other purposes.
The FCC hopes to auction the license plate of the 24GHz frequency band for 5G use. The agency believes—almost certainly—the more bandwidth available in the band, the more valuable the license and the higher the possible bid.
To this end, the FCC has developed rules to encourage the use of the 24GHz frequency band. One of them is the adoption of the operability requirements of the entire 24GHz frequency band. The FCC has also established a sharing framework that allows part of the 24GHz frequency band to be used for terrestrial wireless operations and fixed satellite service (FSS) ground stations.
In addition, in order to prepare for the unplanned future auction, the FCC refused to set pre-auction restrictions on the amount of spectrum (not only the 24GHz frequency band, but also the 47GHz frequency band) that the applicant organization can obtain in the auction. Similarly, the committee also proposed to remove the 1250MHz pre-auction restrictions on the 28GHz, 37GHz and 39GHz bands.
The next bandwidth auction in the United States is for the 28GHz frequency band and is scheduled to start in November this year.
Regulation in Canada and Mexico
Canadian wireless communication companies are frustrated with the country's spectrum auction plan. Canada plans to auction 600MHz spectrum for 5G in 2019, auction 3.5GHz spectrum in 2020, and auction millimeter wave spectrum in 2021 (the frequency has not been specified). Operators hope to start providing commercial 5G services in 2020, and they want to use the 3.5GHz spectrum to do so. They argued that the 3.5GHz auction should be advanced to 2019. The minister responsible for overseeing Canadian telecommunications regulations recently responded that the government does not consider changing the auction schedule.
At the same time, Mexico announced its intention to allocate the 600MHz frequency band for 5G services. According to multiple reports, the plan will require the relocation of 48 digital terrestrial television stations.
Test/trial
You may think that you have already made a 5G call. You know, as long as two people are on one end and talk to each other, this is a phone call. you are wrong. As AT&T and Verizon announced the opening of fixed wireless 5G New Radio (NR) services this summer, and many companies around the world have also announced that they will provide mobile 5G services before the end of this year, we still have a lot of tests and trials to do.
This is also the reason why Nokia and T-Mobile announced that they had completed what seemed to be the first two-way wireless 5G data session on a 5G NR system compliant with 3GPP standards. Recall that it is reasonable that 5G NR is considered to be enhanced 4G instead of true 5G. The 5G NR standard has been adopted, but the entire industry is still adjusting the 5G standard process.
Nokia and T-Mobile said that the test was conducted in the latter's laboratory in Washington State. It uses Nokia AirScale baseband and radio, AirFrame server, and AirScale Cloud RAN running 5G NR 3GPP compatible software.
In late May, the Canadian Shaw Communications Company announced the success of its first trial of 5G technology. The company worked with Nokia, Rohde & Schwarz and CableLabs to test pre-commercial systems at 3.5 GHz and 28 GHz (that is, this was built before the relevant standards were finalized) to test two Interoperability of various frequencies.
The participation of CableLabs is worth noting. The fifth-generation wireless technology will rely more on wired backhaul and dual-mode (cellular/Wi-Fi) work, while the cable industry sees 5G as a trend, which will further tie the fate of wireless and wired providers together.
In April of this year, Rogers Communications of Canada stated that it has conducted some laboratory tests on the 5G system and announced the ongoing test plan with Ericsson, including field trials in Toronto and Ottawa, Canada later this year.
Nokia said it has completed an end-to-end 5G NR data call in a technology trial sponsored by China's Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT). Nokia said that this is a dual-connection call that uses a 3.5GHz 5G NR system and an LTE infrastructure in the 2.1GHz frequency band. User equipment simulation is provided by Prisma Telecom Testing. Nokia explained: "In order to prepare for China's commercial deployment in 2020, dual work in the frequency band below 6GHz will be necessary for wide-area coverage and large-scale IoT connections."
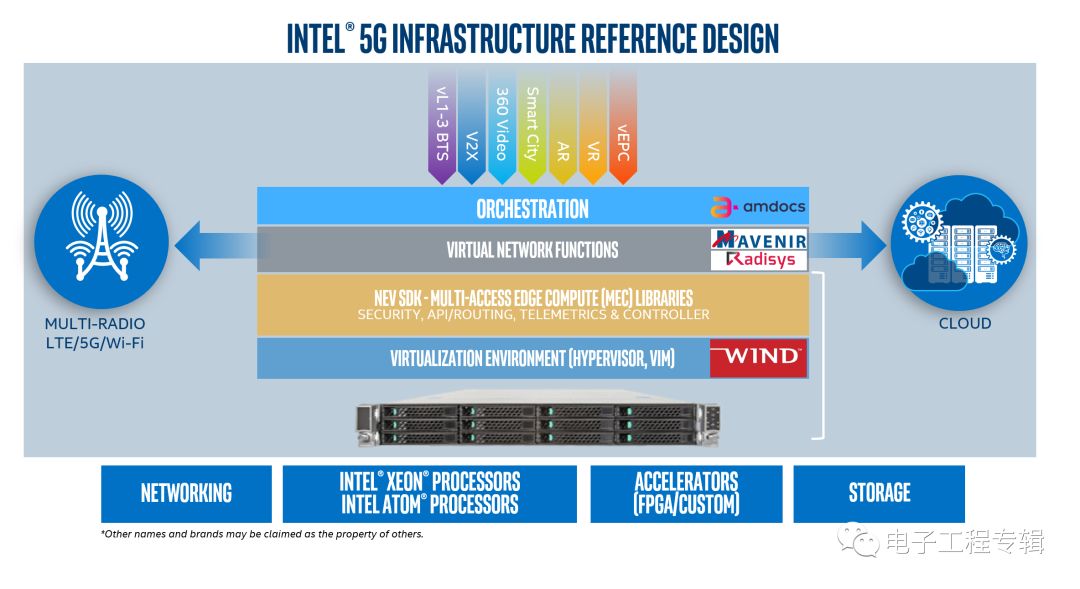
Figure 1: Intel has released a reference design for 5G network infrastructure, which includes contributions from major development partners. Source: Intel.
British wireless operator EE announced that it will start a small test in October, which is said to be the first field test in the UK. Participants will include 10 companies and some residents of Tech City-Tech City, an area near London, has become the city's technology zone. The company will use the 3.5GHz frequency band. According to a report from the news site 5G.co.uk, O2 also plans to conduct trials at the O2 Arena in London later this year.
Don't forget that the development of 5G technology is fundamentally intertwined with application scenarios, and one of the important use cases is the Internet of Things. Taiwan's Youjia Industrial Group (FFG) is planning to develop the first demonstration production line for the so-called "factory of the future." FFG is cooperating with ADLINK to develop the interface between FFG's Robot Operating System (OS) and DDS (Data Distribution Service). This will prepare FFG to use 5G connectivity to achieve automation and the ultimate autonomous factory system.
The following can be said to be a difficult problem in the "test and trial" category, but if someone provides a 5G network reference design, it goes without saying that its network configuration has been tested and tested. Intel has provided a 5G network reference design, which indicates that communication service providers (CSP) can use the reference design to launch 5G services faster (Figure 1). The reference design includes Intel processors and FPGAs, software from Wind River and Radisys, virtualized packet core technology from Mavenir, and network function virtualization (NFV) technology from Amdocs.
product
What is certain is that when operators start to provide 5G mobile services at the end of this year and early next year, there will be no 5G mobile phones on the market, and the first batch of 5G devices will almost certainly be tablets and laptops. Intel said it is working with Sprint to launch 5G networked laptops in 2019. At the recent Taipei International Computer Show, Intel said it is cooperating with Acer, Asus, Dell, Hewlett-Packard, Lenovo and Microsoft.
MediaTek will start selling 5G modem chipsets for 5G NR phones in 2019. The company did not specify a specific date, but said that the chipset will be listed six months earlier than originally planned. MediaTek said the technical details will be announced later, and the spectrum of the chipset will be able to be seen at that time.
It may not be a coincidence that MediaTek’s acceleration schedule keeps pace with China Mobile’s 5G acceleration plan. MediaTek has established development alliances with several other companies including China Mobile and NTT Docomo. China Mobile initially planned to launch commercial 5G mobile communication services in 2020, and earlier this year said it would advance it to a certain time in 2019. At the same time, NTT Docomo still stated that its goal is to establish a "test site" in 2019 and launch commercial 5G mobile communication services in 2020.
Qorvo announced the launch of five new products for 5G base stations: two 2-stage power amplifiers, two integrated front-end modules (FEM) and a broadband driver amplifier. The company said these devices support the 5G frequency range from 3GHz to 39GHz.
At the same time, NXP Semiconductors has also launched a number of devices for the 5G market, that is, a series of high-power RF ICs for 5G base stations operating at various frequencies (Figure 2).

Figure 2: NXP Semiconductors has expanded its GaN and silicon laterally diffused metal oxide semiconductor (Si-LDMOS) product line for use in 5G cellular networks. (Source: NXP)
Anokiwave recently announced the launch of the next-generation products in a new series of 5G-Gen 2 silicon quad-core ICs for base stations. This AWMF-0139 device works at 24/26GHz. The company said that the 5G-Gen 2 series can now support all major 5G millimeter wave frequency bands (24/26GHz, 28GHz and 37/39GHz).
technology
A paper "New 28-GHz transceiver paves the way for future 5G devices" published by Tokyo Institute of Technology introduced a new beam control method. The first instantiated object is a transceiver operating at 28 GHz (one of the millimeter wave frequencies that will be used for 5G mobile communications). The researchers pointed out that most RF phase shifters commonly used in advanced transceivers cannot meet the requirements of 5G transceivers.
The researchers designed a circuit that uses a local oscillator (LO) instead of using multiple RF phase shifters. The new transceiver can move the phase of the LO in steps of 0.04 degrees with very little error. According to the "Science Daily" report, this translates into a beam steering resolution equivalent to 0.1 degrees, which represents an order of magnitude improvement compared to the previous design.
NI will use the channel coding technology developed by Accelercomm. The latter specializes in polar code technology, which is a relatively new error correction coding technology that can be used to replace Turbo codes or low-density parity-check codes (LDPC). Polar codes have been used for 5G channel coding in enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) systems. NI will use Accelercomm's Polar Code IP for its USRP RIO software-defined radio product line, which is suitable for wireless system prototyping.
RJ45 We are manufacturer of RJ45 3U Gold in China, if you want to buy Gold Flash Plated,8P8C with Shield,Shield with EMI please contact us.
The connection sequence of RJ-45 line in common B standard is orange white, orange, green white, blue, blue white, green, brown white and brown. When connecting different equipment, use standard a. the connection sequence is green white, green, orange white, blue, blue white, orange, brown white and brown. Generally, the pressing method of b-mark is commonly used. If you want to make a cross line, one side is a standard, and the other side is b standard.
Working in the data link layer, the switch has a high bandwidth back bus and internal exchange matrix. All ports of the switch are connected to the back bus. After the control circuit receives the data packet, the processing port will look up the address reference table in memory to determine which port the NIC (network card) of destination MAC (hardware address of network card) is attached to. The data packet is quickly transmitted to the destination port through the internal exchange matrix. If the destination MAC does not exist, it will be broadcast to all terminals After the receiving port responds, the switch will "learn" the new address and add it to the internal MAC address table. The switch can also "segment" the network. By comparing the MAC address table, the switch only allows the necessary network traffic through the switch. Through the filter and forward of switch, the conflict domain can be effectively reduced, but it can not divide network layer broadcast, that is, broadcast domain. The switch can transmit data between multiple port pairs at the same time. Each port can be regarded as an independent network segment, and the network equipment connected to it can enjoy all the bandwidth without competing with other devices. When node a sends data to node D, node B can send data to node C at the same time, and these two transmissions enjoy the full bandwidth of the network and have their own virtual connections. If a 10Mbps Ethernet switch is used here, the total flow flux of the switch is equal to 2 × 10Mbps = 20MBps, and the total flow flux of a hub will not exceed 10Mbps when using 10Mbps shared hub. In a word, switch is a kind of network equipment based on MAC address recognition, which can encapsulate and forward data frames. The switch can "learn" the MAC address and store it in the internal address table. By establishing a temporary exchange path between the originator and the target receiver of the data frame, the data frame can reach the destination address directly from the source address.
RJ45 3U Gold,Gold Flash Plated,8P8C with Shield,Shield with EMI
ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.atkconnectors.com